Neurodevelopment
A differentiated chimpanzee cortical neurosphere from induced pluripotent stem cells. Photo by Andrew Field.
Neurodevelopment
The cerebral cortex has expanded in size and complexity in primates. We are taking experimental and computational approaches to understand the molecular innovations that enabled primate-specific brain attributes. We establish cerebral cortex organoids from human, chimpanzee, orangutan, and rhesus pluripotent stem cells to gain insight into how genomic differences influence gene expression, brain development and susceptibility to disease.
Human specific segmental duplications are an important source of new DNA in our genome and many of these “Seg Dups” are recurrently deleted and/or further duplicated in patients with neurodevelopmental disorders. We recently discovered a new family of NOTCH-related genes (NOTCH2NLA, -B, -C) in a disease-associated Seg Dup on human chromosome 1 and showed that altering the gene dosage of NOTCH2NL affects the balance between neural stem cell proliferation and neurogenesis using cerebral organoids. Ongoing research is aimed at understanding the genetic diversity of NOTCH2NL alleles in the human population and their association with neurological disorders as well as mechanistic exploration of the role of NOTCH2NL in cortical neurogenesis, neuronal subtype specification and neuronal function using pluripotent stem cell derived brain organoids.
We have also used transcriptional profiling of human and ape cerebral cortex organoids to identify primate-specific long non-coding (lnc) RNA that show exquisite cell type specificity. Ongoing work is aimed at further characterizing these lncRNAs and exploring their use in non-invasive monitoring of cerebral organoid differentiation and function in close collaboration with other Braingeneers researchers.
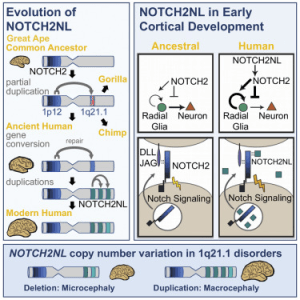
Notch2NL Graphical abstract (from Fiddes et al. 2018)
Key Publications
Structurally conserved primate LncRNAs are transiently expressed during human cortical differentiation and influence cell-type-specific genes
AR Field, FMJ Jacobs, IT Fiddes, APR Phillips, AM Reyes-Ortiz, E LaMontagne, L Whitehead, V Meng, JL Rosenkrantz, M Olsen, M Hauessler, S Katzman, SR Salama, D Haussler
Stem cell reports 12 (2), 245-257
Human-Specific NOTCH2NL Genes Affect Notch Signaling and Cortical Neurogenesis
IT Fiddes, GA Lodewijk, M Mooring, CM Bosworth, AD Ewing, et al.
Cell 173 (6), 1356-1369. e22
Funding
National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), NIH